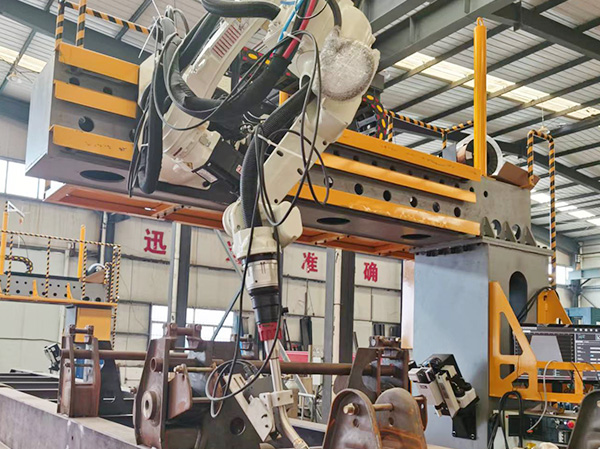
Laser cutting technology, as an advanced manufacturing process, plays a crucial role in modern industrial production. Due to its high efficiency, precision, and strong adaptability, it is widely used in the processing of various materials. Laser cutting machines achieve fast and accurate cutting of materials by focusing high-energy density laser beams, demonstrating excellent processing performance for both metallic and non-metallic materials.
metallic material
In the field of metal processing, laser cutting machines have shown great flexibility and efficiency. It can handle materials ranging from lightweight stainless steel plates to thicker carbon steel and alloy materials. For stainless steel plates with a thickness of 1-5 millimeters, a medium power laser cutting machine can complete the task. For thicker materials, such as 8-20mm carbon steel or 12mm stainless steel, high-power fiber laser cutting machines or CO2 laser cutting machines are required to ensure cutting speed and quality. Carbon steel is an ideal choice for laser cutting due to its excellent beam absorption characteristics. In addition, non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, and titanium are also frequent customers of laser cutting machines. Despite their high reflectivity of light, modern laser systems can effectively cope and achieve high-quality cutting.
Non metallic materials
Laser cutting technology is not limited to metals, it is also applicable to a wide range of non-metallic materials. Plastic products, including ABS, acrylic (PMMA), polycarbonate (PC), etc., can achieve smooth and non fused edges through laser cutting, making them particularly suitable for products that require fine processing. Laser cutting machines can also process paper, wood, leather, fabrics, and numerous organic glass materials, providing new creative possibilities for industries such as advertising signage, handicraft production, and clothing design.
composite material
With the development of materials science, composite materials are widely used due to their unique properties, such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) and glass fiber reinforced plastics (GFRP). These materials have important applications in aerospace, automotive manufacturing, sports equipment and other fields, and laser cutting machines, with their high degree of control and precise positioning ability, can accurately cut these complex materials while reducing delamination and thermal damage, maintaining the overall strength and integrity of the materials.
Features and advantages
The core advantages of laser cutting lie in its high precision, high speed, and minimal heat affected area. Due to the non-contact nature of laser cutting, it does not cause tool wear or leave pressure marks on the surface of the workpiece, ensuring the smoothness and quality of the cutting surface. In addition, the focusing characteristics of the laser beam make the cutting seam extremely narrow, which is particularly important for parts that require high-precision machining. The integration of automation and robotics technology further enhances the flexibility and efficiency of laser cutting, making it easy to process complex shapes and three-dimensional structures.
In summary, laser cutting machines, with their wide applicability, almost cover all the main material categories required for processing in modern industry. Whether in traditional manufacturing or high-tech industries, they play an irreplaceable role in promoting the continuous progress and innovation of manufacturing technology.